MHC-II binding predictions - Tutorial
How to obtain predictions
This website provides access to predictions of peptide binding to MHC class II molecules. The screenshot below illustrates the steps necessary to make a prediction.
Each of the steps is described in more detail below.
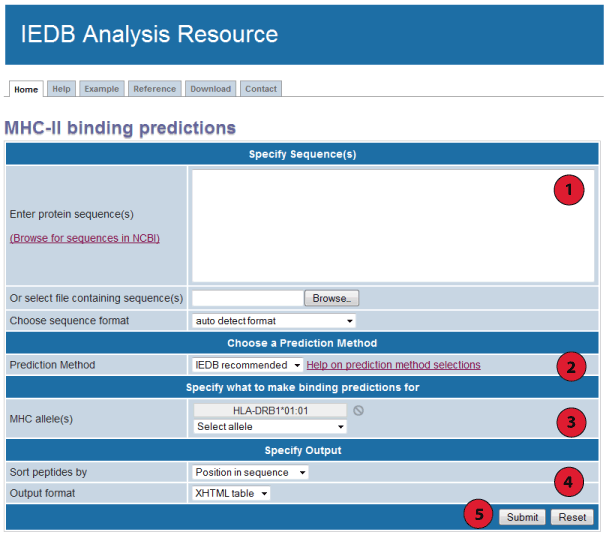
1. Specify sequences:
First specify the sequences you want to scan for binding peptides. The sequences
should either be entered directly into the textarea field labeled "Enter protein sequence(s),
or can be taken from a file that has to be uploaded using the button labeled "Browse". Please
enter no more then 200 FASTA sequences or upload file size less than or equal to 10 MB per query.
The sequences can be supplied in three different formats:
- Space separated sequences
- One continuous sequence
- FASTA format
The format of the sequences can be specified explicitly using the list box
labeled "Choose sequence format". If that list box is set to "auto detect format", the
input will be interpreted as FASTA if an opening ">" character is found, or as
a continuous sequence otherwise.
All sequences have to be amino acids specified in single letter code (
ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY).
2. Choose a prediction method:
The prediction method list box allows choosing between eight currently implemented
MHC class II binding prediction methods:
IEDB recommended,
Consensus method,
Average relative binding (arb),
combinatorial library (manuscript in preparation),
NN-align (netMHCII-2.2),
SMM-align (netMHCII-1.1),
Sturniolo, and
NetMHCIIpan.
The default selection IEDB Recommended is provided.
Based on availability of predictors and previously observed predictive performance,
this selection tries to use the best possible method for a given MHC molecule.
The selection IEDB Recommended uses the Consensus approach, combining NN-align, SMM-align,
and CombLib if any corresponding predictor is available for the molecule, otherwise NetMHCIIpan is used.
The expected predicted performance for MHC-II binding methods in decreasing order are:
Consensus > NetMHCIIpan > NN-align > SMM-align > CombLib.
The expected predictive performances are based on two large scale evaluations of
the performance of the MHC class II binding predictions:
a
2008 study based on over 10,000 binding affinities and
a
2010 study based on over 40,000 binding affinities.
Supplementary information for evaluation of predictive tools are available for
2008 and
2010 studies.
Of note, we fully expect the IEDB recommendation to change as we perform larger benchmarks
of newly developed methods on blind datasets to determine an accurate assessment of prediction quality.
3. Specify what to make predictions for:
Predictions are limited to alleles that are currently covered by specific
prediction methods. Selection of a particular prediction method will generate
a list of available alleles. User can then choose a specific allele to make
predictions.
4. Specify the output:
The menus in this section change how the prediction output is displayed. Using the
"Sort peptides by" listbox, the results can be presorted by the order of the peptides
in their source sequence (default) or by their predicted affinity.
To reuse the prediction results in an external program, it is possible to
retrieve the predictions in a plain text format. To do this, choose "Text file" in the
output format listbox.
5. Submit the prediction:
This one is easy. Click the submit button, and a result screen similar to the one below should appear.
Interpreting prediction output
Below is a screenshot of a prediction output page, with three relevant sections
marked that are described in more detail below.
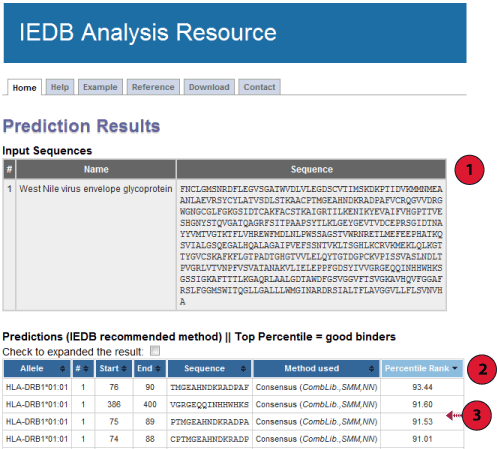
1. Input Sequences:
This table displays the sequences and their names extracted from the user input.
If no names were assigned by the user (which is only possible in FASTA format),
the sequences are numbered in their input order (sequence 1, sequence 2, ...).
2. Prediction output table:
Each row in this table corresponds to one peptide binding prediction. The columns
contain the allele the prediction was made for, the position of the peptide in the
input sequences (in the format [Sequence #]: [Start Position] - [End Position]), the core sequence, the predicted score and percentile rank for ARB, combinatorial library, SMM_align and Sturniolo. The last column is the percentile rank for the consensus method. Table can be sorted by clicking on the table column headers.
3. Interpreting predicted results:
The predicted output is given in units of IC
50nM for ARB, combinatorial library and SMM_align.
Therefore a lower number indicates higher affinity. As a rough guideline, peptides with IC
50values <50 nM are considered high affinity, <500 nM intermediate affinity and <5000 nM low affinity. Most known epitopes have high or intermediate affinity. Some
epitopes have low affinity, but no known T-cell epitope has an IC
50
value greater than 5000.
The prediction result for Sturniolo is given as raw score. Higher score indicates higher affinity.
For each peptide, a percentile rank for each of the four methods (ARB, combinatorial library, SMM_align and Sturniolo) is generated by comparing the peptide's score against the scores of five million random 15 mers selected from SWISSPROT database. A small numbered percentile rank indicates high affinity. The median percentile rank of the four methods were then used to generate the rank for consensus method.
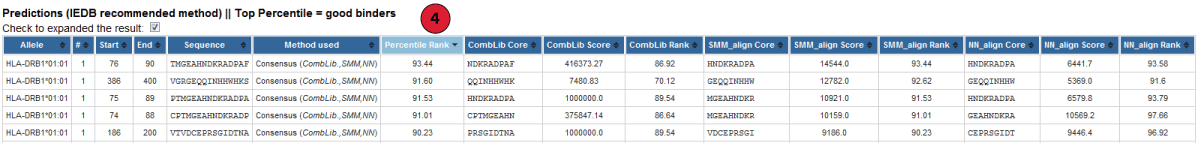
4. Predicted results:
NetMHCIIpan method is used when Consensus and other methods such as SMM_align, NN_align, COMBLIB and/or Sturniolo are not available for a particular allele.
However, f only one or two of these methods are available, NetMHCIIpan is used as second or third method.
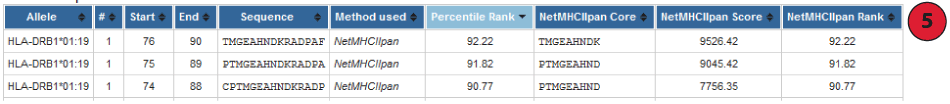
5. Default prediction output table:
By default prediction result is collapsed to show only the Percentile Rank when the Consensus method is used. The table can be expended to display the individual score of different methods used by checking box above result table.




